Diffusion
• The spontaneous movement of a substance from a region of high concentration to the region of low concentration is called diffusion.
• Some substances like carbon dioxide or oxygen can move across the cell membrane by a process called diffusion. Cell also obtains nutrition from the environment.
Osmosis
• The movement of water molecules through selectively permeable membrane along the concentration gradient is called osmosis.
• Plant cell tend to obtain water through osmosis.
Plasmolysis
• When a living plant cell loses water through osmosis there is shrinkage or contraction of the contents of the cell away from the cell wall. This phenomenon is known as plasmolysis.
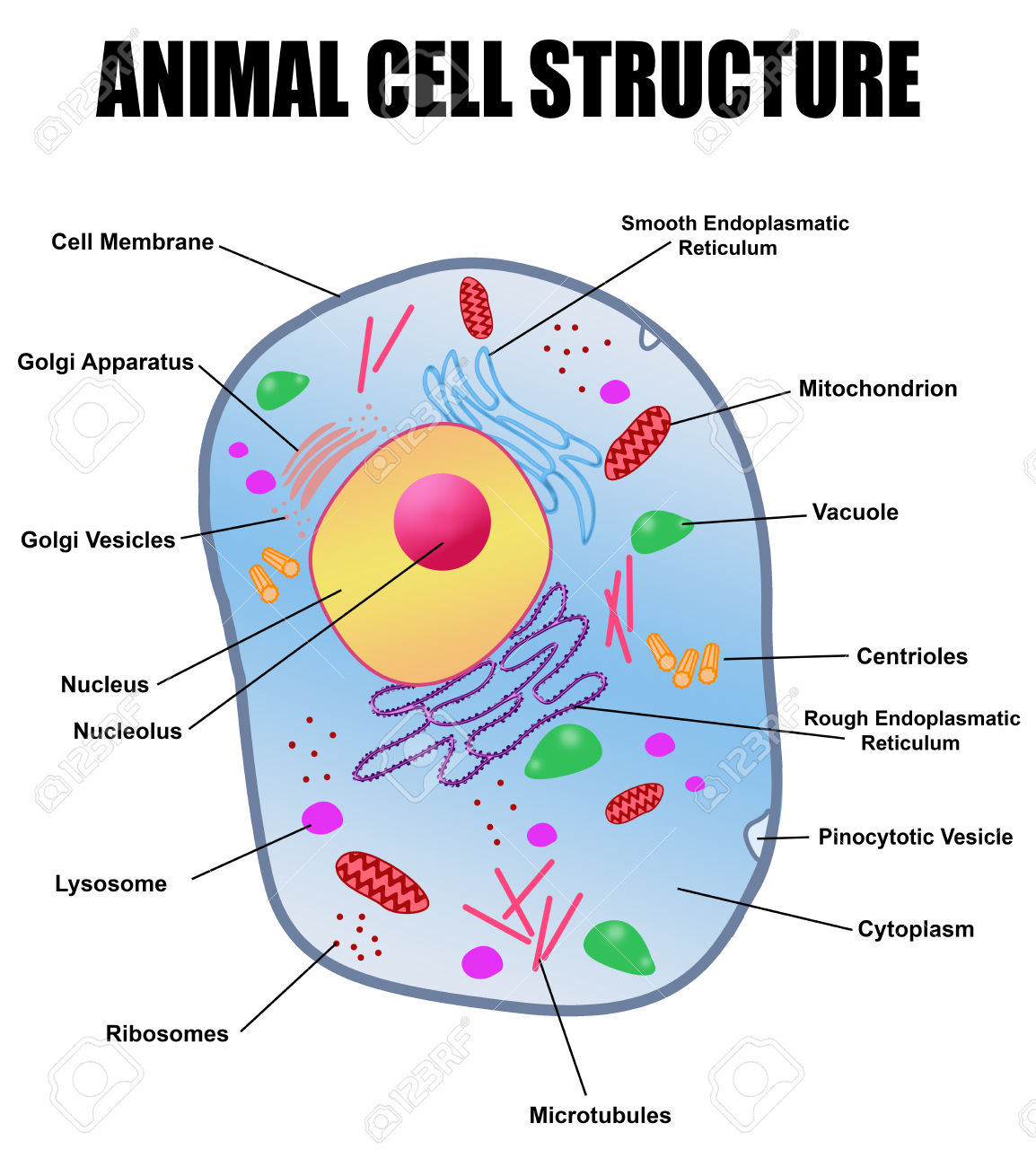
Nucleus
• It is called the brain of the cell as it controls all the activities of cell.
→ Composition of Nucleus
• The nucleus has a double layered covering called nuclear membrane.
• The nuclear membrane has pores which allow the transfer of material from inside the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
• The nucleus contains chromosomes, which are visible as rod-shaped structures only when the cell is about to divide.
→ Functions of chromosomes
• Chromosomes contain information for inheritance of features from parents to next generation in the form of DNA (Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid) molecules .Chromosomes are composed of DNA and protein.
• DNA molecules contain the information necessary for constructing and organising cells.
• Functional segments of DNA are called genes.
• In non-dividing cell, this DNA is present as part of chromatin material.
• Chromatin material is visible as entangled mass of thread like structures. Whenever the cell is about to divide, the chromatin material gets organised into chromosomes and perform cell division.
→ Functions of Nucleus
• The nucleus plays a central role in cellular reproduction. It is the process by which a single divides and forms two new cells.
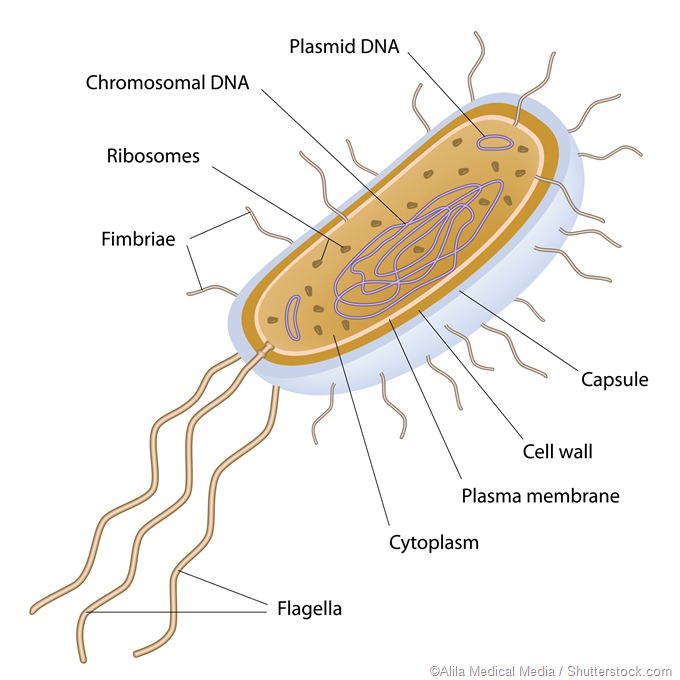
Nucleoid
• In some organisms like bacteria, the nuclear region of the cell may be poorly defined due to the absence of a nuclear membrane.
• Such an undefined nuclear region containing only nucleic acids is called a nucleoid.